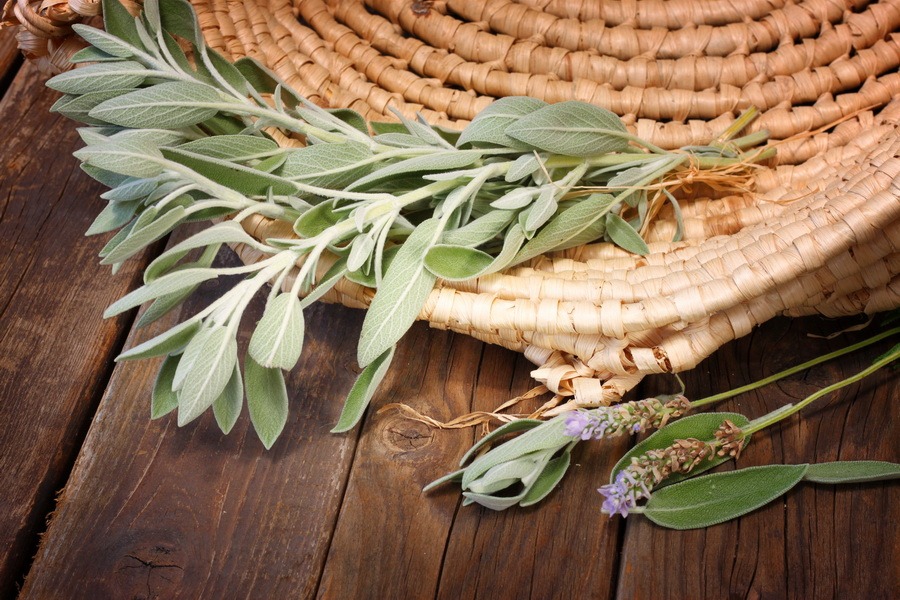
Salvia officinalis, often referred to simply as sage, is one of the most famous aromatic and medicinal plants.
In folk and official medicine, pronounced antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and hemostatic properties have been proven. Sage increases the secretory functions of the digestive tract. The high content of phytohormones contributes to the fact that healing sage is recommended for neuroses, headaches, stress. Official medicine recommends sage extracts as a remedy for the gums and to fight inflammation in the oral cavity. For some time now, there has been scientific evidence that sage extracts are effective in treating Alzheimer’s disease and high cholesterol.
In contrast to clary sage, medicinal sage is only used to a limited extent in food production. However, the herb is used as a condiment for fish, poultry, meat, and vegetables. It gives salads, canned food and drinks a special character- with a slight bitter note. Sage is added to food in small quantities. Its aroma is rich and powerful, which allows it to drown out more subtle smells. An excess of this spice should be avoided. In terms of taste, it can be combined well with marjoram, rosemary, oregano, thyme or juniper. In Western European cuisine, it is believed that the taste of food and beverages becomes more pronounced and distinctive when the sage is added to those dishes or drinks. In addition, sage extract is a very good preservative.
The CO2 extract from Salvia officinalis is a brown, viscous liquid with a strong characteristic aroma. The extract begins to thicken at temperatures below + 15 ° C and practically loses its flowability; the viscosity of the extract decreases as the temperature rises. The most valuable properties of medicinal sage are found in a complex of terpenoids that make up the essential oil.
Chart 1. Main components of CO2 sage extract
| NAME | CONTENT IN% OF THE AMOUNT OF VOLATILE COMPONENTS | EFFECT |
|---|---|---|
| α and β – thujone | 29,7 | The hallucinogenic effect has not been scientifically proven. However, it negatively affects the neurotransmitter receptors. |
| Camphor | 14 | Treats colds, coughs, decongestant, stimulates blood circulation. Effective against fungal infections. Sedative. Has a pronounced warming effect, helps with cramps. It is used against acne, pimples, itching. |
| Manool | 8,8 | Replacement for ambergris in the perfume industry. It has pronounced anti-inflammatory and antifungal effects. |
| α and β – caryophyllene | 8,7 | Used in perfumery as a natural fragrance. |
| α and β-pinene | 2,8 | Locally irritating, antiseptic expectorant. |
| m-mento-1,8-diene | 2 | It has antiseptic and antibacterial properties. Bactericidal. |
| Borneo | 1,7 | Antiarrhythmic, analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory effect. |
In cosmetics, the CO2 extract of the medicinal sage is used as follows:
– in the composition of toothpastes as an antibacterial, antiseptic and deodorant additive;
– in skin care products for combination skin and oily skin;
– in agents for reducing pores and normalizing sebum production;
– in cleansers for the care of damaged and tired skin;
– Medicinal sage is traditionally used in dentistry as a pain reliever;
When preparing fatty dishes, the CO2 extract improves the taste and stimulates the digestive process.
Salvia officinalis is currently practically non-existent in the wild, although it is one of the most frequently cultivated medicinal plants in southern European countries. In Russia, it was grown in the Krasnodar and Stavropol territories, as well as in the Crimea. It is often found growing wild in vegetable gardens. In addition to medicinal sage, there is also clary sage, but these two types of sage differ both in terms of their organoleptic properties and the direction of application as well as in their biological effectiveness. The main purpose of processing sage leaves is to obtain essential oil.
Even at the time of Hippocrates, healing sage was considered a source of strength and youth.
Chart 2. Application rates, recommendations for the use and storage of CO2 sage extract
| Food usage rates | Item А100: 0.001-0.005% (10-50g per ton) Water-soluble microemulsions EMA1: 0.1-0.5% (1-5l per 1000l or 1-5ml per liter) Water-soluble microemulsions EMA5: 0.02-0.1% (0.2-1l per 1000l or 0.2-1ml per liter) |
| Application rates in cosmetics | Item А10: 1-3% Item А100: 0.1-0.3% Item EMA1: 10-30% Item EMA5: 2-6% |
| Recommendations for use | It is recommended to add CO2 extracts in the final stages of preparation, in the cooling phase of the end product. |
| Storage advice | It is recommended to store CO2 extracts in a closed container in a cool room and avoid direct sunlight. |